22230 - 22230
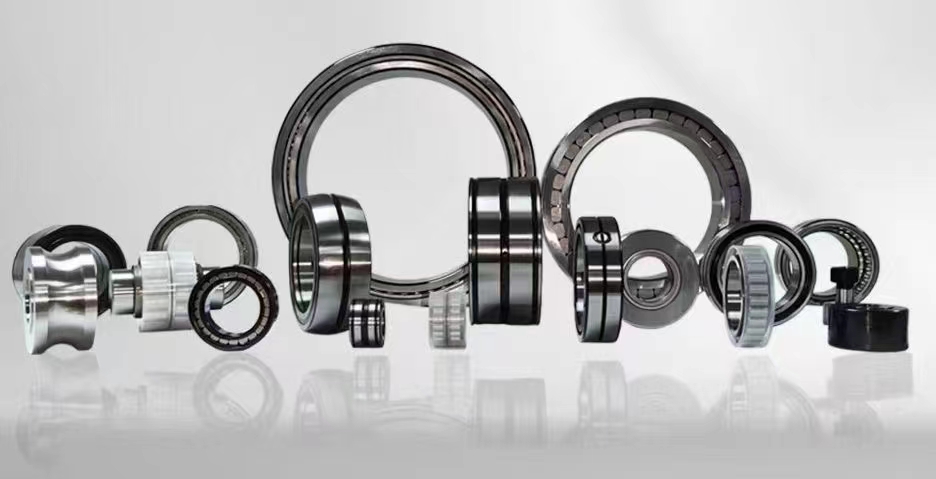
Bearingtypes
Most bearings in high cycle operations need periodic lubrication and cleaning, and may require adjustment to minimise the effects of wear.
Bearings saw use for holding wheel and axles. The bearings used there were plain bearings that were used to greatly reduce friction over that of dragging an object by making the friction act over a shorter distance as the wheel turned.
Although long bearing life is often desirable, it is sometimes not necessary. Harris describes a bearing for a rocket motor oxygen pump that gave several hours life, far in excess of the several tens of minutes life needed.[1]
A bearing is a device to allow constrained relative motion between two or more parts, typically rotation or linear movement. Bearings may be classified broadly according to the motions they allow and according to their principle of operation as well as by the directions of applied loads they can handle.
8 types ofbearing
The first plain and rolling-element bearings were wood, but ceramic, sapphire, or glass were also used, and steel, bronze, other metals, ceramics, and plastic (e.g., nylon, polyoxymethylene, polytetrafluoroethylene, and UHMWPE) are all common today. A "jeweled" pocket watch uses stones to reduce friction, and allow more precise time keeping. Even old materials can have good durability. As examples, wood bearings can still be seen today in old water mills where the water provides cooling and lubrication.
A second source of motion is elasticity in the bearing itself. For example, the balls in a ball bearing are like stiff rubber, and under load deform from round to a slightly flattened shape. The race is also elastic and develops a slight dent where the ball presses on it.
Leonardo da Vinci is often credited with drawing the first roller bearing around the year 1500. However, Agostino Ramelli is the first to have published sketches of roller and thrust bearings.[2] An issue with ball bearings is the balls rub against each other, causing additional friction, but rubbing can be prevented by enclosing the balls in a cage. The captured, or caged, ball bearing was originally described by Galileo in the 1600s. The mounting of bearings into a set was not accomplished for many years after that. The first patent for a ball race was by Philip Vaughan of Carmarthen in 1794.
It sounds like there's something loose that's causing the clicking/clunking sound. It happens more when it's hot outside or after driving the car a good bit.
Search results for: '5000 160' ; 25-911-5000-PSI/BAR-PMC, NoShok, 25-911-5000-PSI/BAR-PMC, 2-1/2" STAINLESS CASE GLYCERINE FILLED. Call for ...
However, there are many applications where a more suitable bearing can improve efficiency, accuracy, service intervals, reliability, speed of operation, size, weight, and costs of purchasing and operating machinery.
The stiffness of a bearing is how the distance between the parts which are separated by the bearing varies with applied load. With rolling element bearings this is due to the strain of the ball and race. With fluid bearings it is due to how the pressure of the fluid varies with the gap (when correctly loaded fluid bearings are typically stiffer than rolling element bearings).
The earliest recovered example of a bearing is a wooden ball bearing supporting a rotating table from the remains of the Roman Nemi ships in Lake Nemi, Italy. The wrecks were dated to 40 AD.[4][5]
3 main types of bearings
Allowable play varies greatly depending on the use. As example, a wheelbarrow wheel supports radial and axial loads. Axial loads may be hundreds of newtons force left or right, and it is typically acceptable for the wheel to wobble by as much as 10 mm under the varying load. In contrast, a lathe may position a cutting tool to ±0.02 mm using a ball lead screw held by rotating bearings. The bearings support axial loads of thousands of newtons in either direction, and must hold the ball lead screw to ±0.002 mm across that range of loads.
74HB/40-75 KD 1-1/2 GRN from ABUS USA at RS. ... ABUS USA 74HB/40-75 KD 1-1/2 GRN. Padlock,Plastic Covered,1-1/2in W,Shackle 1/4in D 3in H 3/4in W ...
Reducing friction in bearings is often important for efficiency, to reduce wear and to facilitate extended use at high speeds and to avoid overheating and premature failure of the bearing. Essentially, a bearing can reduce friction by virtue of its shape, by its material, or by introducing and containing a fluid between surfaces or by separating the surfaces with an electromagnetic field.
Many bearings require periodic maintenance to prevent premature failure, although some such as fluid or magnetic bearings may require little maintenance.
The oldest instance of the bearing principle dates to the Egyptians when they used tree trunks under sleds.[2] There are also Egyptian drawings of bearings used with hand drills.[3]
1. m. almohadilla (‖ cojín sobre el que se cose). 2. m. Pieza de hierro con que se sujetan los carriles a las traviesas del ferrocarril. 3. m.
Friedrich Fischer's idea from the year 1883 for milling and grinding balls of equal size and exact roundness by means of a suitable production machine formed the foundation for creation of an independent bearing industry.
Mar 18, 2012 — Yes, either can cause a misfire. Both at the same time? Pretty coincidental I'd think. socal pat is offline. socal pat.
The modern, self-aligning design of ball bearing is attributed to Sven Wingquist of the SKF ball-bearing manufacturer in 1907, when he was awarded Swedish patent No. 25406 on its design.
Bearing mechanicalEngineering
Bearing life is often much better when the bearing is kept clean and well-lubricated. However, many applications make good maintenance difficult. For example bearings in the conveyor of a rock crusher are exposed continually to hard abrasive particles. Cleaning is of little use because cleaning is expensive, yet the bearing is contaminated again as soon as the conveyor resumes operation. Thus, a good maintenance program might lubricate the bearings frequently but clean them never.
Bearing mechanicaldiagram
Purchase FR6 6 Zone Coolant Flow Regulator 2.625 Gpm Per Zone - Multi Zone Flow Regulators From DME. Visit Us To Get Started!
Fluid and magnetic bearings can potentially give indefinite life. In practice, there are fluid bearings supporting high loads in hydroelectric plants that have been in nearly continuous service since about 1900 and which show no signs of wear.
Types ofbearingwith Diagram
Find the exact bearing or power transmission products you need with our bearing finder and online interchange catalog. Filter parts and components by size in ...
A patent on ball bearings, reportedly the first, was awarded to Jules Suriray, a Parisian bicycle mechanic, on 3 August 1869. The bearings were then fitted to the winning bicycle ridden by James Moore in the world's first bicycle road race, Paris-Rouen, in November 1869.[6]
Plain bearings use surfaces in rubbing contact, often with a lubricant such as oil or graphite. A plain bearing may or may not be a discrete device. It may be nothing more than the bearing surface of a hole with a shaft passing through it, or of a planar surface that bears another (in these cases, not a discrete device); or it may be a layer of bearing metal either fused to the substrate (semi-discrete) or in the form of a separable sleeve (discrete). With suitable lubrication, plain bearings often give entirely acceptable accuracy, life, and friction at minimal cost. Therefore, they are very widely used.
In the early 1980s, Pacific Bearing's founder, Robert Schroeder, invented the first bi-material plain bearing which was size interchangeable with linear ball bearings. This bearing had a metal shell (aluminum, steel or stainless steel) and a layer of Teflon-based material connected by a thin adhesive layer.[citation needed]
The first practical caged-roller bearing was invented in the mid-1740s by horologist John Harrison for his H3 marine timekeeper. This uses the bearing for a very limited oscillating motion but Harrison also used a similar bearing in a truly rotary application in a contemporaneous regulator clock.
Henry Timken, a 19th century visionary and innovator in carriage manufacturing, patented the tapered roller bearing, in 1898. The following year, he formed a company to produce his innovation. Through a century, the company grew to make bearings of all types, specialty steel and an array of related products and services.
Combinations of these can even be employed within the same bearing. An example of this is where the cage is made of plastic, and it separates the rollers/balls, which reduce friction by their shape and finish.
Some applications apply bearing loads from varying directions and accept only limited play or "slop" as the applied load changes. One source of motion is gaps or "play" in the bearing. For example, a 10 mm shaft in a 12 mm hole has 2 mm play.
Rolling element bearing life is determined by load, temperature, maintenance, lubrication, material defects, contamination, handling, installation and other factors. These factors can all have a significant effect on bearing life. For example, the service life of bearings in one application was extended dramatically by changing how the bearings were stored before installation and use, as vibrations during storage caused lubricant failure even when the only load on the bearing was its own weight.[1] Bearing life is statistical: several samples of a given bearing will often exhibit a bell curve of service life, with a few samples showing significantly better or worse life. Bearing life varies because microscopic structure and contamination vary greatly even where macroscopically they seem identical.
Types ofbearing mechanical
Neck Attachment Screws, short, 40mm ... Price per piece. ... All prices are in EURO and include German Tax/VAT. Tax Free purchases for non-EU Countries! If your ...
For plain bearings some materials give much longer life than others. Some of the John Harrison clocks still operate after hundreds of years because of the lignum vitae wood employed in their construction, whereas his metal clocks are seldom run due to potential wear.
Today, bearings are used in a variety of applications. Ultra high speed bearings are used in dental hand pieces, aerospace bearings are used in the Mars Rover, and flexure bearings are used in optical alignment systems.
Erich Franke invented and patented the wire race bearing in 1934. His focus was on a bearing design with a cross section as small as possible and which could be integrated into the enclosing design. After World War II he founded together with Gerhard Heydrich the company Franke & Heydrich KG (today Franke GmbH) to push the development and production of wire race bearings.
The aim of Funk's Race4Change effort is to raise awareness of microfinance and the change it can inspire. The third world is poor because of the developed ...
Product description. Deep groove ball bearings are particularly ... Supplier number: SKF 6201-Z. Show more features. Inner diameter: 12 mm; Width: 10 ...
Types of bearings pdf
Flexure bearings bend a piece of material repeatedly. Some materials fail after repeated bending, even at low loads, but careful material selection and bearing design can make flexure bearing life indefinite.
Smoothie/Yogurt Base Freezer, counter model, air or water cooled, self-contained refrigeration, 1 head, 20 qt. mix capacity, welded steel frame, stainless steel exterior, AccuFreeze solid-state control, visual mix out system, 1 HP dasher, 1 HP compressor, UL, NSF, cUL, Made in USA
af:Laer (toestel) az:Yastıq (texnika) bs:Ležaj cs:Ložisko de:Lager (Maschinenelement) et:Laager es:Rodamiento eo:Lagro fa:یاتاقان fr:Palier (mécanique) ko:베어링 hi:बेयरिंग it:Cuscinetto (meccanica) he:מיסב lt:Guolis (mechanika) hu:Csapágy nl:Lager (mechanica) ja:軸受 pl:Łożysko (mechanika) pt:Rolamento ro:Cuzinet ru:Подшипник simple:Bearing (mechanical) sk:Ložisko (technika) sl:Ležaj fi:Laakeri sv:Lager (teknik) th:ตลับลูกปืน tr:Yatak (makina elemanı) uk:Підшипник vi:Ổ lăn zh:轴承
Different bearing types have different operating speed limits. Speed is typically specified as maximum relative surface speeds, often specified ft/s or m/s. Rotational bearings typically describe performance in terms of the product DN where D is the diameter (often in mm) of the bearing and N is the rotation rate in revolutions per minute.
Thus, there are many types of bearings, with varying shape, material, lubrication, principal of operation, and so on. For example, rolling-element bearings use spheres or drums rolling between the parts to reduce friction; reduced friction allows tighter tolerances and thus higher precision than a plain bearing, and reduced wear extends the time over which the machine stays accurate. Plain bearings are commonly made of varying types of metal or plastic depending on the load, how corrosive or dirty is the environment, and so on. In addition, bearing friction and life may be altered dramatically by the type and application of lubricants. For example, a lubricant may improve bearing friction and life, but for food processing a bearing may be lubricated by an inferior food-safe lubricant to avoid food contamination; in other situations a bearing may be run without lubricant because continuous lubrication is not feasible, and lubricants attract dirt that damages the bearings.
Generally there is considerable speed range overlap between bearing types. Plain bearings typically handle only lower speeds, rolling element bearings are faster, followed by fluid bearings and finally magnetic bearings which are limited ultimately by centripetal force overcoming material strength.



 8613869596835
8613869596835