20 Ceramic Bearing Manufacturers in 2024 - ceramic bearing
When a solid spacer and pinion nut are used, shims control pinion bearing preload. The pinion nut is torqued to a specific value found in the service manual.
Cam followervs lifter
The main components of a cam follower are an outer ring, seal slide plate, cage, needle roller, and stud. The outer ring is thick-walled, and can either be spherical or cylindrical. A cylindrical outer ring absorbs distortion and assists in lightening a balanced load. The main design difference between cam followers and roller followers is that cam followers have a built-in mounting shaft.
Types ofcamandfollowerpdf
With a collapsible spacer, only tighten the pinion nut in small increments. Then measure the pinion preload by turning the pinion nut with an inch-pound torque wrench.
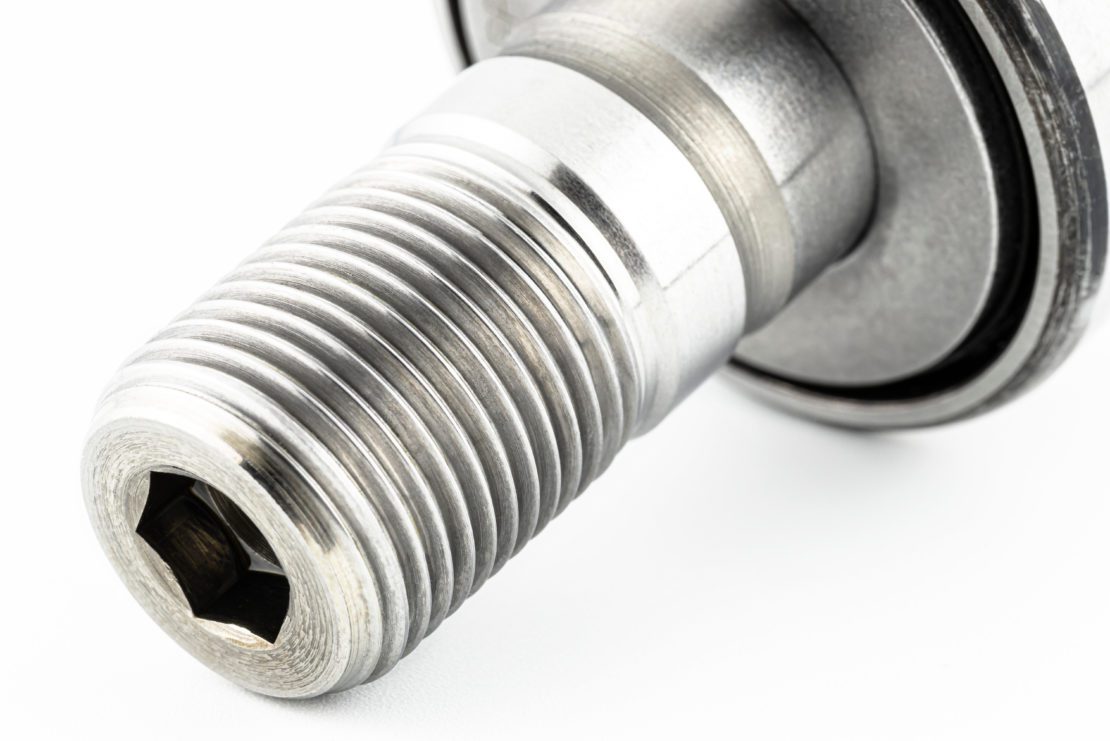

Its purpose is to help reduce frictional loss in the valvetrain, as well as prevent stress within the camshaft; stress is sometimes generated in the camshaft when it exceeds its own load capacity.
Cam and roller followers are similar in terms of load rating and other performance capability factors. They are both rigid and compact, and designed to handle high-speed rotation. Neither is inherently better or worse than the other.
Cam followerbearing
If ring gear runout is excessive, check the ring gear mounting and differential case runout. If not a mounting problem, replace either the ring gear and pinion or the case as needed.
PINION BEARING PRELOAD. - The pinion bearing preload is frequently adjusted by torquing the pinion nut to compress a collapsible spacer. The more the pinion nut is torqued, the more the spacer will compress to increase the preload or tightness of the bearings.
CASE BEARING PRELOAD. - The case bearing preload is the amount of force pushing the differential case bearings together. As with pinion bearing preload, it is critical.
CamandfollowerDiagram
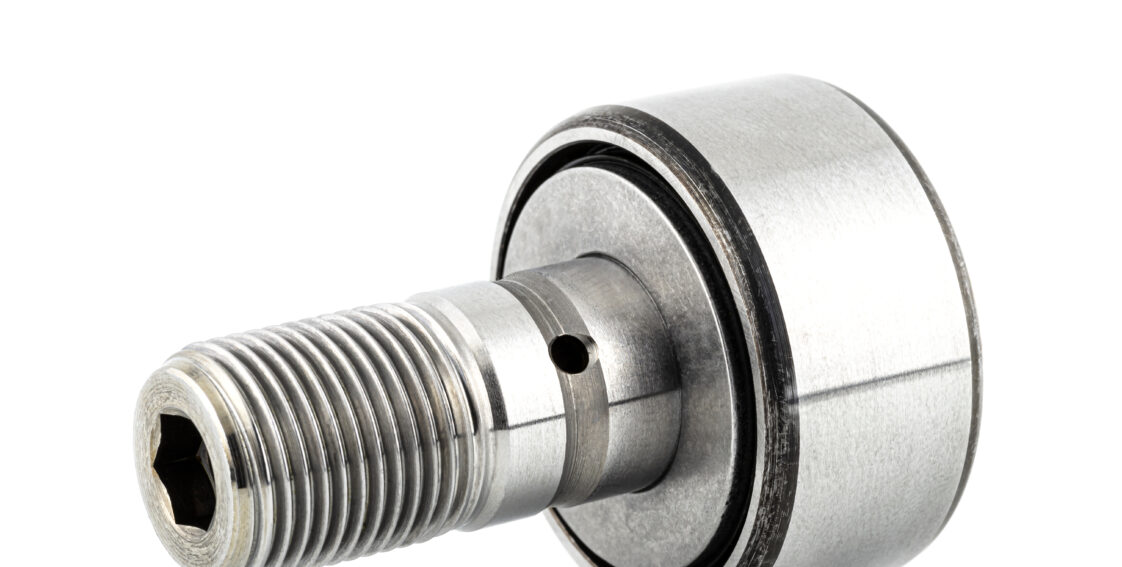
Although they are different components, “cam follower” and “roller follower” are sometimes used interchangeably. The job of both types of parts is to transform the rotary motion of a cam into linear motion.
CamandfollowerPDF
RING GEAR RUNOUT. - The ring gear runout is the amount of wobble or side-to-side movement produced when the ring gear is rotated. Ring gear runout must not be beyond the manufacturer's specifications.
Universal Bearings is an industry-leading manufacturing of precision needle bearing products. We produce needle roller bearings, including cam follower and roller follower bearings, that meet rigid manufacturing tolerances. We can discuss your requirements with you, and help you determine which solution is best for your application. Contact us today to get started.
In this article, we’ll explain the differences between a roller follower and cam follower, as well as provide an overview of the characteristics, advantages, and common industry applications of each.
A roller follower is made up of an outer ring, seal, needle roller, inner ring, side plate, and cage. There are two types of roller followers: separable (has separable inner rings) and non-separable (inner ring cannot be separated). The outer ring is thick-walled to bear impact. The needle rollers and cage prevent skewing and boost rotation performance.
To measure ring gear runout, mount a dial indicator against the back of the ring gear (fig. 5-20). The indicator stem should be perpendicular to the ring gear surface. Then turn the ring gear and note the indicator reading. If the ring gear is within specifications, locate a position on the ring gear that indicates ONE HALF of the maximum runout on the gauge. Mark the gear at that point. Then rotate the ring gear until the teeth on the opposite side of the gear from the mark are in mesh with the pinion gear.
What is a cam followerinacar
As the gears operate, they produce friction and heat. This makes the gears expand, reducing the clearance between the meshing teeth of the gears. Without backlash, the ring and pinion teeth can jam into each other and fail in a very short period of time. However, too much ring and pinion backlash can cause gear noise (whirring, roaring, or clunking).
RING AND PINION BACKLASH. - The ring and pinion backlash refers to the amount of space between the meshing teeth of the gears. Backlash is needed to allow for heat expansion
When adjusting nuts are used, the nuts are typically tightened until all of the play is out of the bearings. Then each nut is tightened a specific portion of a turn to preload the bearings. This is done when adjusting backlash.
Track followers are suitable for a number of industrial uses, especially where space is available in stationary gas and oil engines, as well as aircraft engines. Other applications include carrier systems, bookbinding machines, pallet changers, sliding forks in automated warehouses, conveyors, automatic coating machines, and tool changers.
Cam followertypes
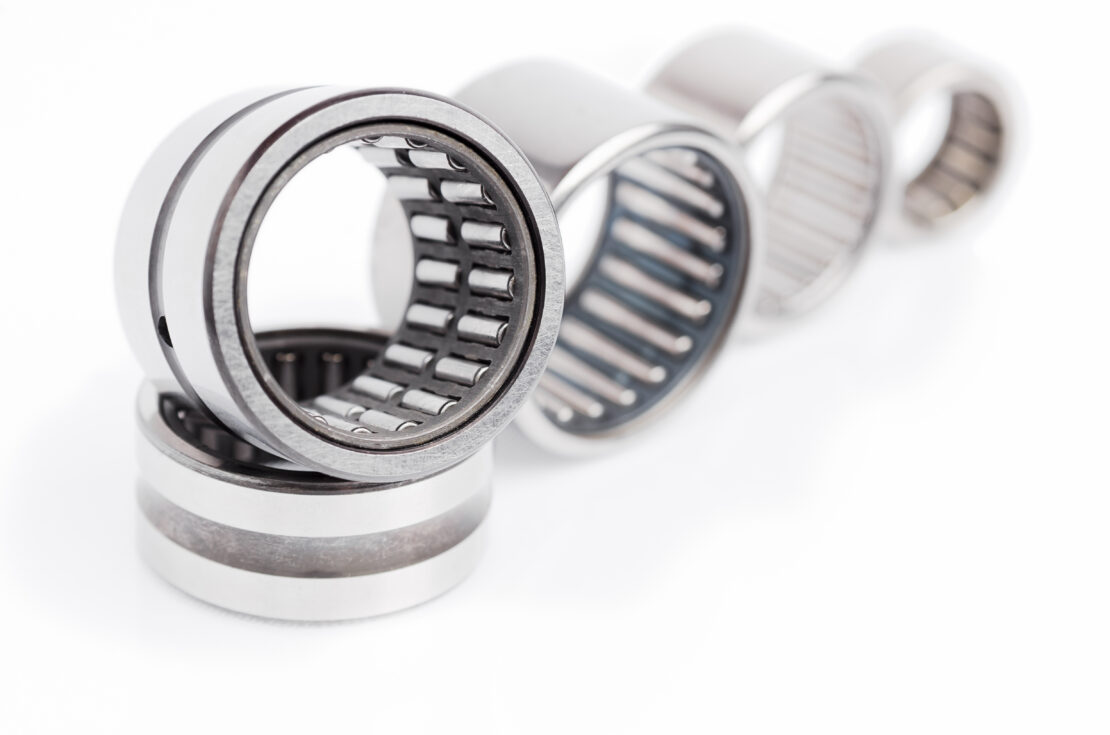

Camandfollowerexamples
Cam followers are rigid, compact bearings distinguished by the presence of a shaft. Just like roller followers, they convert rotary motion into linear motion and help maintain precision by reducing wear and sliding friction on the cam and track.
To set pinion bearing preload, use a holding tool to keep the pinion gear stationary. Then a breaker bar or torque wrench can be used to tighten the pinion nut.
Cam followers are frequently used in industrial applications that use conveyors or process transfer lines. They’re widely found in power generation, metal processing, transportation, food processing, and packaging. They’re also used in some of the same types of machines as roller followers, including pallet changers, automated coating machines, conveyors, automatic warehouse sliding forks, and tool changers.
If preload is too low (bearings too loose), differential case movement and ring and pinion gear noise can result. If preload is too high (bearings too tight), bearing overheating and failure can result.
PINION GEAR DEPTH. - The pinion gear depth refers to the distance the pinion gear extends into the carrier. Pinion depth affects where the pinion gear teeth meshes with the ring gear teeth. Pinion gear depth is commonly adjusted by varying shim thickness on the pinion gear and bearing assembly.
The choice comes down to the specific constraints of the design. The most significant difference is that cam followers include a shaft, while a track follower must attach to a shaft that’s already in place. The existing stud of cam followers is useful if there’s a flat surface such that the bearing can be mounted within the design. Roller followers, with their separable or non-separable inner rings, can be matched to an existing shaft to avoid extra weight and product cost.
When shims are used, a feeler gauge is used to check side clearance between the case bearing and the carrier. This action will let you calculate the correct shim thickness to preload the case bearings. Refer to the service manual for special equipment and procedures.



 8613869596835
8613869596835