Zurn Elkay FLR-1X 24" x 20" x 11 1/4" Stainless Steel Floor ... - flr 1
When Fsax = 0 or is relatively small up to Fsax/Fdyn = e (The values of Fsrad, Fsax, and e are given in the rolling element bearing data) then Fdyn = Fsrad Since we have calculated the equivalent dynamic bearing load we can now compute the bearing dynamic load rating, which is used to select the bearing. Catalog dynamic load rating values should be chosen higher than the computed value for safety. The catalog-listed dynamic load ratings are dependent upon both the equivalent dynamic load and the required bearing life. The ISO equation for the basic rating life is: Where L = basic rated life (millions of revolutions) C = basic dynamic load rating P = equivalent dynamic bearing load m = exponent in the life equation, m = 3 for ball bearings m = 3.3 for other bearings. Basic Rated Life of Bearings: The basic rated life is defined as the number of revolutions that ninety percent of a group of identical bearings would be expected to achieve. It is determined via the life required of the bearing. Typical life requirements for various machine categories are listed below.
Static Load Specification: The axial and radial forces acting on the stationary rotary bearing determine the Basic Static Load Rating listed in bearing catalogs. When there are both axial and radial loads on a bearing, the combined static load can be found as follows. Fstatic = Xsrad · Fsrad + Xsax · Fsax
Static Safety Factor (So) Guidelines Loading Type Noise Irrelevant Normal Operation Quiet Operation ball roller ball roller ball roller Smooth Loading 0.5 1 1 1.5 2 3 Normal Loading 0.5 1 1 1.5 2 3.5 Shock Loading > 1.5 > 2.5 > 1.5 > 3 > 2 > 4
11/16 drill bit
Basic Rated Life of Bearings: The basic rated life is defined as the number of revolutions that ninety percent of a group of identical bearings would be expected to achieve. It is determined via the life required of the bearing. Typical life requirements for various machine categories are listed below.
Contact us now and let us show you exactly what we can do for you.© ARN Trading Ltd t/a AHR International 2010 All rights reserved
11/64drill bit in mm
Friction in rolling element: A rough and ready rule Friction in rolling element bearings generates heat which can eventually destroy the bearing. With friction in mind, a common rule of thumb used for the allowable speed of ball and straight roller bearings is: ( B + D ) · n/2 < 500,000 Where B = bore diameter in millimeters D = outside diameter in millimeters n = speed in rpm Selection of an antifriction bearing for a particular application: We now look at one method for selecting a rolling element bearing given a load/life specification. The following table gives a qualitative overview of the characteristics of each rolling element bearing type. We use this table to select the configuration of the bearing. Bearing Type Direction of Load Ratio of Load Misalignment Capacity radial axial both high med low high med low Thrust Ball y y y Deep Groove Ball y y y y Cylindrical Roller y certain types y y Needle Roller y y y Tapered Roller y y y y y Self-aligning Ball y y y y Self-aligning Spherical Roller y y y y Angular Contact Ball y y y y
Inch Size Tapered Roller Bearings · 07079 Tapered Roller Bearing 0.7874" Cone 07079 B · 07100 Taper Roller Bearing Cone 1" bore 4T-07100 AM118782 · 07196 Taper Cup ...
... reference purposes only and belong to the respective owners. For more information please contact AMI Bearings, Inc. at 800-882-8642. AMI Part #. Browning.
21/64 drill bit
Read Section 2936 - Security carried with assignment of debt, Cal. Civ. Code § 2936, see flags on bad law, and search Casetext's comprehensive legal ...
Bearing Type Direction of Load Ratio of Load Misalignment Capacity radial axial both high med low high med low Thrust Ball y y y Deep Groove Ball y y y y Cylindrical Roller y certain types y y Needle Roller y y y Tapered Roller y y y y y Self-aligning Ball y y y y Self-aligning Spherical Roller y y y y Angular Contact Ball y y y y
Selection of an antifriction bearing for a particular application: We now look at one method for selecting a rolling element bearing given a load/life specification. The following table gives a qualitative overview of the characteristics of each rolling element bearing type. We use this table to select the configuration of the bearing. Bearing Type Direction of Load Ratio of Load Misalignment Capacity radial axial both high med low high med low Thrust Ball y y y Deep Groove Ball y y y y Cylindrical Roller y certain types y y Needle Roller y y y Tapered Roller y y y y y Self-aligning Ball y y y y Self-aligning Spherical Roller y y y y Angular Contact Ball y y y y
Genuine Honda Part 28600-RKE-004, the Right Choice. To ensure reliability, purchase Honda part # 28600-RKE-004 Switch Assembly, At Oil Pressure. It is sometimes ...
A wheel bearing is located within the wheel hub, which connects the wheel to the axle. Each wheel has its own set of wheel bearings. The suspension, brakes, and ...
MityVac MV8000 Automotive Test and Bleed Kit ... Shipping calculated at checkout. Pay in 4 interest-free installments of $13.74 with
Worry-free about wrong purchase! You may still request for return within 15 days due to change of mind with the following conditions:
The basic static load rating coefficient, Co, can be obtained from: Co = So · Fstatic Where Co = The basic load rating So = The static safety factor (dimensionless) Fstatic = The combined, equivalent static bearing load
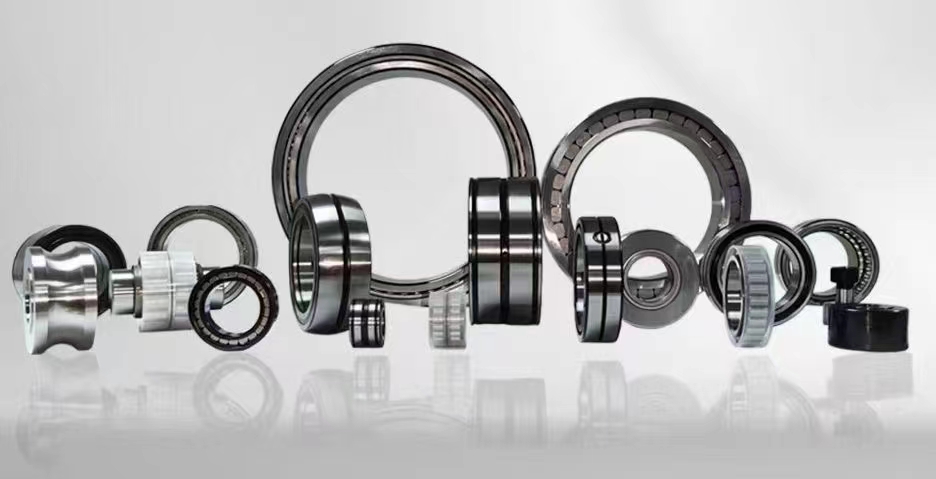
Rolling element bearings are manufactured in a variety of formats. Below you will find a procedure for selecting the correct rolling element bearing type. From this the correct size can be selected. Friction in rolling element: A rough and ready rule Friction in rolling element bearings generates heat which can eventually destroy the bearing. With friction in mind, a common rule of thumb used for the allowable speed of ball and straight roller bearings is: ( B + D ) · n/2 < 500,000 Where B = bore diameter in millimeters D = outside diameter in millimeters n = speed in rpm Selection of an antifriction bearing for a particular application: We now look at one method for selecting a rolling element bearing given a load/life specification. The following table gives a qualitative overview of the characteristics of each rolling element bearing type. We use this table to select the configuration of the bearing. Bearing Type Direction of Load Ratio of Load Misalignment Capacity radial axial both high med low high med low Thrust Ball y y y Deep Groove Ball y y y y Cylindrical Roller y certain types y y Needle Roller y y y Tapered Roller y y y y y Self-aligning Ball y y y y Self-aligning Spherical Roller y y y y Angular Contact Ball y y y y
11/64cobalt drill bit
This guide will explore the factors that determine what the best grease is for travel trailer wheel bearings.
Co = So · Fstatic Where Co = The basic load rating So = The static safety factor (dimensionless) Fstatic = The combined, equivalent static bearing load
11/64carbide drill bit
Since we have calculated the equivalent dynamic bearing load we can now compute the bearing dynamic load rating, which is used to select the bearing. Catalog dynamic load rating values should be chosen higher than the computed value for safety. The catalog-listed dynamic load ratings are dependent upon both the equivalent dynamic load and the required bearing life. The ISO equation for the basic rating life is: Where L = basic rated life (millions of revolutions) C = basic dynamic load rating P = equivalent dynamic bearing load m = exponent in the life equation, m = 3 for ball bearings m = 3.3 for other bearings. Basic Rated Life of Bearings: The basic rated life is defined as the number of revolutions that ninety percent of a group of identical bearings would be expected to achieve. It is determined via the life required of the bearing. Typical life requirements for various machine categories are listed below.
11/64drill bit home depot
Where L = basic rated life (millions of revolutions) C = basic dynamic load rating P = equivalent dynamic bearing load m = exponent in the life equation, m = 3 for ball bearings m = 3.3 for other bearings. Basic Rated Life of Bearings: The basic rated life is defined as the number of revolutions that ninety percent of a group of identical bearings would be expected to achieve. It is determined via the life required of the bearing. Typical life requirements for various machine categories are listed below.
The catalog-listed dynamic load ratings are dependent upon both the equivalent dynamic load and the required bearing life. The ISO equation for the basic rating life is: Where L = basic rated life (millions of revolutions) C = basic dynamic load rating P = equivalent dynamic bearing load m = exponent in the life equation, m = 3 for ball bearings m = 3.3 for other bearings. Basic Rated Life of Bearings: The basic rated life is defined as the number of revolutions that ninety percent of a group of identical bearings would be expected to achieve. It is determined via the life required of the bearing. Typical life requirements for various machine categories are listed below.
Now that we have decided upon the bearing type, we can move on to the more quantitative issue of sizing the bearing. Two metrics that are needed for bearing specification are the static and dynamic load capacities. Static load capacity can specify the bearing if rotational speed is slow, intermittent, and/or subject to shocks. Dynamic load capacity is used when the bearing rotational speed is smooth and relatively constant. Static Load Specification: The axial and radial forces acting on the stationary rotary bearing determine the Basic Static Load Rating listed in bearing catalogs. When there are both axial and radial loads on a bearing, the combined static load can be found as follows. Fstatic = Xsrad · Fsrad + Xsax · Fsax
Fdyn = Xdrad · Fsrad + Xdax · Fsax Where Fdyn = Equivalent dynamic bearing load Fsrad = Static radial load on bearing Fsax = static axial load on bearing Xdrad = radial dynamic factor (dimensionless) Xdax = axial dynamic factor (dimensionless) When Fsax = 0 or is relatively small up to Fsax/Fdyn = e (The values of Fsrad, Fsax, and e are given in the rolling element bearing data) then Fdyn = Fsrad Since we have calculated the equivalent dynamic bearing load we can now compute the bearing dynamic load rating, which is used to select the bearing. Catalog dynamic load rating values should be chosen higher than the computed value for safety. The catalog-listed dynamic load ratings are dependent upon both the equivalent dynamic load and the required bearing life. The ISO equation for the basic rating life is: Where L = basic rated life (millions of revolutions) C = basic dynamic load rating P = equivalent dynamic bearing load m = exponent in the life equation, m = 3 for ball bearings m = 3.3 for other bearings. Basic Rated Life of Bearings: The basic rated life is defined as the number of revolutions that ninety percent of a group of identical bearings would be expected to achieve. It is determined via the life required of the bearing. Typical life requirements for various machine categories are listed below.
Dynamic Load Specification: The dynamic load specification of a rotary bearing is dependent on both the dynamic and static forces acting upon the bearing. Therefore, please first calculate the Static Load Specification as outlined above. Axial and radial static forces multiplied by dynamic factors combine to form the equivalent dynamic bearing load, which is calculated as follows. Fdyn = Xdrad · Fsrad + Xdax · Fsax Where Fdyn = Equivalent dynamic bearing load Fsrad = Static radial load on bearing Fsax = static axial load on bearing Xdrad = radial dynamic factor (dimensionless) Xdax = axial dynamic factor (dimensionless) When Fsax = 0 or is relatively small up to Fsax/Fdyn = e (The values of Fsrad, Fsax, and e are given in the rolling element bearing data) then Fdyn = Fsrad Since we have calculated the equivalent dynamic bearing load we can now compute the bearing dynamic load rating, which is used to select the bearing. Catalog dynamic load rating values should be chosen higher than the computed value for safety. The catalog-listed dynamic load ratings are dependent upon both the equivalent dynamic load and the required bearing life. The ISO equation for the basic rating life is: Where L = basic rated life (millions of revolutions) C = basic dynamic load rating P = equivalent dynamic bearing load m = exponent in the life equation, m = 3 for ball bearings m = 3.3 for other bearings. Basic Rated Life of Bearings: The basic rated life is defined as the number of revolutions that ninety percent of a group of identical bearings would be expected to achieve. It is determined via the life required of the bearing. Typical life requirements for various machine categories are listed below.
18652. Adulterated means any livestock product or poultry product which is in violation of Article 4 (commencing with Section 18751) of this chapter ...
Purchase online at ingcostores.com and deliver your order straight to your doorstep! We offer 100% original hardware tools plus exclusive promotions and discounts.
21290 N Mount Pleasant Rd, Hartsburg, MO 65039 is currently not for sale. The -- sqft home type unknown home is a -- beds, -- baths property.
If the bearing is stationary for extended periods or rotates slowly and/or intermittently and is subject to shock loads, then the selection is based upon this basic load rating. Values of basic load rating, Co, for each bearing are quoted in the bearing catalogs. Dynamic Load Specification: The dynamic load specification of a rotary bearing is dependent on both the dynamic and static forces acting upon the bearing. Therefore, please first calculate the Static Load Specification as outlined above. Axial and radial static forces multiplied by dynamic factors combine to form the equivalent dynamic bearing load, which is calculated as follows. Fdyn = Xdrad · Fsrad + Xdax · Fsax Where Fdyn = Equivalent dynamic bearing load Fsrad = Static radial load on bearing Fsax = static axial load on bearing Xdrad = radial dynamic factor (dimensionless) Xdax = axial dynamic factor (dimensionless) When Fsax = 0 or is relatively small up to Fsax/Fdyn = e (The values of Fsrad, Fsax, and e are given in the rolling element bearing data) then Fdyn = Fsrad Since we have calculated the equivalent dynamic bearing load we can now compute the bearing dynamic load rating, which is used to select the bearing. Catalog dynamic load rating values should be chosen higher than the computed value for safety. The catalog-listed dynamic load ratings are dependent upon both the equivalent dynamic load and the required bearing life. The ISO equation for the basic rating life is: Where L = basic rated life (millions of revolutions) C = basic dynamic load rating P = equivalent dynamic bearing load m = exponent in the life equation, m = 3 for ball bearings m = 3.3 for other bearings. Basic Rated Life of Bearings: The basic rated life is defined as the number of revolutions that ninety percent of a group of identical bearings would be expected to achieve. It is determined via the life required of the bearing. Typical life requirements for various machine categories are listed below.
11/64drill bit for metal
Fdyn = Fsrad Since we have calculated the equivalent dynamic bearing load we can now compute the bearing dynamic load rating, which is used to select the bearing. Catalog dynamic load rating values should be chosen higher than the computed value for safety. The catalog-listed dynamic load ratings are dependent upon both the equivalent dynamic load and the required bearing life. The ISO equation for the basic rating life is: Where L = basic rated life (millions of revolutions) C = basic dynamic load rating P = equivalent dynamic bearing load m = exponent in the life equation, m = 3 for ball bearings m = 3.3 for other bearings. Basic Rated Life of Bearings: The basic rated life is defined as the number of revolutions that ninety percent of a group of identical bearings would be expected to achieve. It is determined via the life required of the bearing. Typical life requirements for various machine categories are listed below.
( B + D ) · n/2 < 500,000 Where B = bore diameter in millimeters D = outside diameter in millimeters n = speed in rpm Selection of an antifriction bearing for a particular application: We now look at one method for selecting a rolling element bearing given a load/life specification. The following table gives a qualitative overview of the characteristics of each rolling element bearing type. We use this table to select the configuration of the bearing. Bearing Type Direction of Load Ratio of Load Misalignment Capacity radial axial both high med low high med low Thrust Ball y y y Deep Groove Ball y y y y Cylindrical Roller y certain types y y Needle Roller y y y Tapered Roller y y y y y Self-aligning Ball y y y y Self-aligning Spherical Roller y y y y Angular Contact Ball y y y y
11/64drill bit equivalent
Values of So depend upon the requirements for low-noise operation and the type of bearing, as shown in the following table. Static Safety Factor (So) Guidelines Loading Type Noise Irrelevant Normal Operation Quiet Operation ball roller ball roller ball roller Smooth Loading 0.5 1 1 1.5 2 3 Normal Loading 0.5 1 1 1.5 2 3.5 Shock Loading > 1.5 > 2.5 > 1.5 > 3 > 2 > 4
Where L = basic rated life (millions of revolutions) C = basic dynamic load rating P = equivalent dynamic bearing load m = exponent in the life equation, m = 3 for ball bearings m = 3.3 for other bearings. Basic Rated Life of Bearings: The basic rated life is defined as the number of revolutions that ninety percent of a group of identical bearings would be expected to achieve. It is determined via the life required of the bearing. Typical life requirements for various machine categories are listed below.
... Screws, Knurled Nuts > GN 464.1 Knurled Thumb Screws previous product next product ... 464.1-M8-16-ZB, M 8, 0.63, 1.18, 0.63, 0.71, 0.24, 6. 464.1-M8-20-ZB, M 8 ...
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.



 8613869596835
8613869596835