The Importance of Bearings in Machinery and Equipment

Bearings are crucial components in machinery and equipment, serving as the interface between moving parts and enabling smooth and efficient operation. They play a vital role in reducing friction, supporting loads, and facilitating rotation, making them essential in a wide range of industries, from automotive and aerospace to manufacturing and construction.
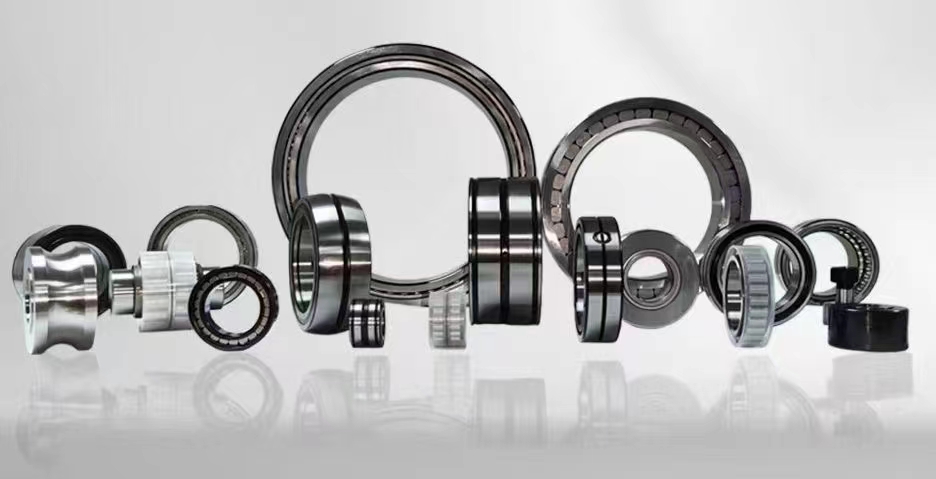
In simple terms, a bearing is a device that allows two parts to move relative to each other with minimal friction. It consists of two main components: the inner ring, which is attached to the rotating shaft, and the outer ring, which is fixed in place. Between these two rings are a set of rolling elements, such as balls or rollers, that allow the inner and outer rings to rotate smoothly against each other.
One of the key benefits of bearings is their ability to reduce friction and wear between moving parts. By providing a smooth surface for rotation, bearings help to minimize heat generation and energy loss, improving the overall efficiency and lifespan of machinery and equipment. This is especially important in high-speed applications, where friction can lead to overheating and premature failure.
Bearings also play a crucial role in supporting loads and maintaining the stability of rotating components. They help to distribute the weight of the load evenly across the contact surface, preventing excessive stress on individual parts and ensuring smooth and reliable operation. This is particularly important in heavy-duty applications, such as automotive engines and industrial machinery, where bearings are subjected to high loads and forces.
In addition to reducing friction and supporting loads, bearings also help to facilitate rotation and motion in machinery and equipment. By allowing parts to move freely in a controlled manner, bearings enable smooth and precise operation, leading to improved performance and productivity. This is essential in precision engineering and manufacturing, where even the slightest deviation in movement can have a significant impact on the quality and accuracy of the final product.
There are several different types of bearings available, each designed for specific applications and operating conditions. The most common types include ball bearings, roller bearings, and plain bearings, each offering unique advantages in terms of load capacity, speed, and durability. Choosing the right type of bearing for a particular application is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity.

Ball bearings are the most widely used type of bearing, known for their high speed and low friction characteristics. They consist of a series of small balls that roll between the inner and outer rings, providing smooth rotation and minimal wear. Ball bearings are commonly used in automotive and industrial applications, where high-speed operation and precise movement are critical.
Roller bearings, on the other hand, are designed to support heavier loads and withstand higher forces. They feature cylindrical or tapered rollers that distribute the load evenly across the contact surface, allowing for greater load capacity and durability. Roller bearings are often used in heavy-duty applications, such as construction equipment and mining machinery, where high loads and harsh operating conditions are common.
Plain bearings, also known as bushings, are another type of bearing that relies on a sliding motion rather than rolling elements. They consist of a smooth surface, such as a metal sleeve or polymer material, that allows for frictionless movement between two parts. Plain bearings are often used in low-speed and high-load applications, where simplicity and reliability are more important than speed and precision.
In conclusion, bearings are essential components in machinery and equipment, serving as the interface between moving parts and enabling smooth and efficient operation. They help to reduce friction, support loads, and facilitate rotation, leading to improved performance and longevity. By choosing the right type of bearing for a particular application, manufacturers can ensure optimal efficiency and reliability in their products.



 8613869596835
8613869596835